Pleistocene
The Pleistocene often colloquially referred to as the Ice Age) is the geological epoch which lasted from about 2,588,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the world's most recent period of repeated glaciations. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology.
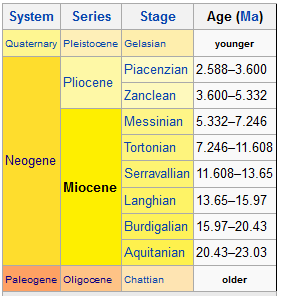
The Pleistocene is the first epoch of the Quaternary Period or sixth epoch of the Cenozoic Era. In the ICS timescale, the Pleistocene is divided into four stages or ages, the Gelasian, Calabrian, Middle Pleistocene (unofficially the 'Chibanian') and Upper Pleistocene (unofficially the 'Tarantian'). In addition to this international subdivision, various regional subdivisions are often used.
The Pleistocene often colloquially referred to as the Ice Age) is the geological epoch which lasted from about 2,588,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the world's most recent period of repeated glaciations. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology.
The Pleistocene is the first epoch of the Quaternary Period or sixth epoch of the Cenozoic Era. In the ICS timescale, the Pleistocene is divided into four stages or ages, the Gelasian, Calabrian, Middle Pleistocene (unofficially the 'Chibanian') and Upper Pleistocene (unofficially the 'Tarantian'). In addition to this international subdivision, various regional subdivisions are often used.
Paleogeography and climate
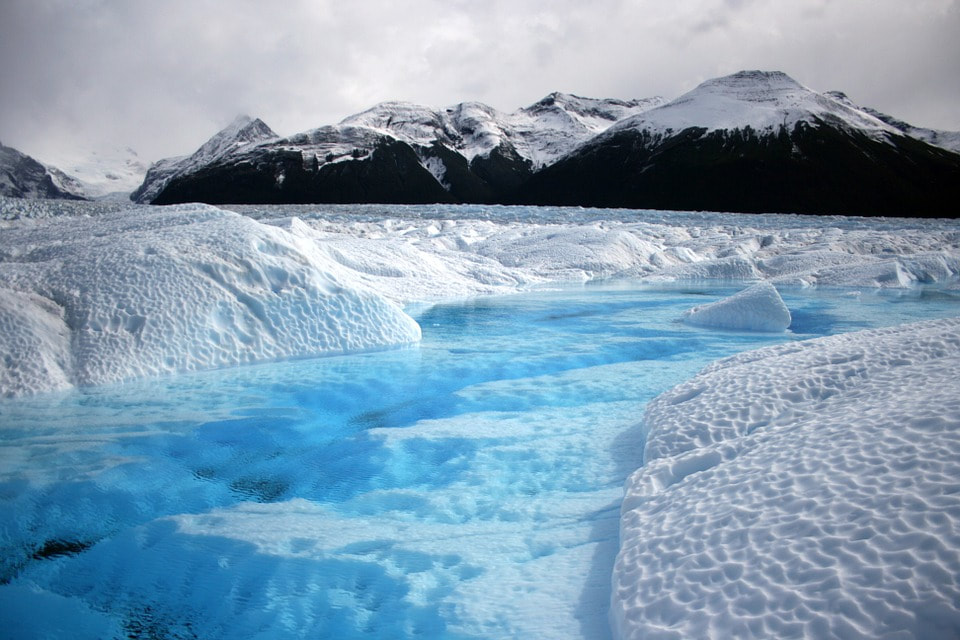
The maximum extent of glacial ice in the north polar area during the Pleistocene period. The modern continents were essentially at their present positions during the Pleistocene, the plates upon which they sit probably having moved no more than 100 km relative to each other since the beginning of the period.
Glacial features
Pleistocene climate was marked by repeated glacial cycles in which continental glaciers pushed to the 40th parallel in some places. It is estimated that, at maximum glacial extent, 30% of the Earth's surface was covered by ice. In addition, a zone of permafrost stretched southward from the edge of the glacial sheet, a few hundred kilometres in North America, and several hundred in Eurasia. The mean annual temperature at the edge of the ice was −6 °C (21 °F); at the edge of the permafrost, 0 °C (32 °F).
The effects of glaciation were global. Antarctica was ice-bound throughout the Pleistocene as well as the preceding Pliocene. The Andes were covered in the south by the Patagonian ice cap. There were glaciers in New Zealand and Tasmania. The current decaying glaciers of Mount Kenya, Mount Kilimanjaro, and the Ruwenzori Range in east and central Africa were larger. Glaciers existed in the mountains of Ethiopia and to the west in the Atlas mountains.
In the northern hemisphere, many glaciers fused into one. The Cordilleran ice sheet covered the North American northwest; the east was covered by the Laurentide. The Fenno-Scandian ice sheet rested on northern Europe, including Great Britain; the Alpine ice sheet on the Alps. Scattered domes stretched across Siberia and the Arctic shelf. The northern seas were ice-covered.
South of the ice sheets large lakes accumulated because outlets were blocked and the cooler air slowed evaporation. When the Laurentide ice sheet retreated, north central North America was totally covered by Lake Agassiz. Over a hundred basins, now dry or nearly so, were overflowing in the North American west. Lake Bonneville, for example, stood where Great Salt Lake now does. In Eurasia, large lakes developed as a result of the runoff from the glaciers. Rivers were larger, had a more copious flow, and were braided. African lakes were fuller, apparently from decreased evaporation. Deserts on the other hand were drier and more extensive. Rainfall was lower because of the decreases in oceanic and other evaporation.
It has been estimated that during the Pleistocene, the East Antarctic Ice Sheet thinned by at least 500 meters, and that thinning since the Last Glacial Maximum is less than 50 meters and probably started after ca 14 ka.
Fauna
Both marine and continental faunas were essentially modern but with many more large land mammals such as Mammoths, Mastodons, Diprotodon, Smilodon, tiger, lion, Aurochs, Short-faced bear, giant sloths, Gigantopithecus and others. Isolated places such as Australia, Madagascar, New Zealand and islands in the Pacific saw the evolution of large birds and even reptiles such as the Elephant bird, moa, Haast's eagle, Quinkana, Megalania and Meiolania.
The severe climatic changes during the ice age had major impacts on the fauna and flora. With each advance of the ice, large areas of the continents became totally depopulated, and plants and animals retreating southwards in front of the advancing glacier faced tremendous stress. The most severe stress resulted from drastic climatic changes, reduced living space, and curtailed food supply. A major extinction event of large mammals (megafauna), which included mammoths, mastodons, saber-toothed cats, glyptodons, the woolly rhinoceros, various giraffids, such as the Sivatherium; ground sloths, Irish elk, cave bears, Gomphothere, dire wolves, and short-faced bears, began late in the Pleistocene and continued into the Holocene. Neanderthals also became extinct during this period. At the end of the last ice age, cold-blooded animals, smaller mammals like wood mice, migratory birds, and swifter animals like whitetail deer had replaced the megafauna and migrated north.
The extinctions hardly affected Africa but were especially severe in North America where native horses and camels were wiped out.
Humans
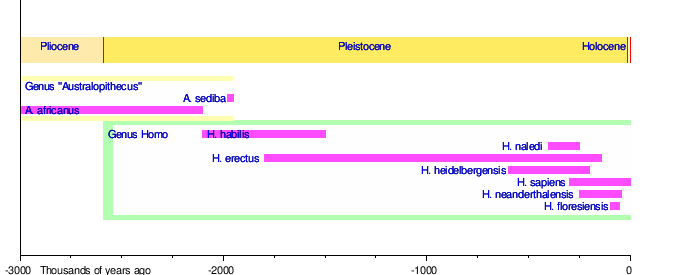
The evolution of anatomically modern humans took place during the Pleistocene. In the beginning of the Pleistocene Paranthropus species are still present, as well as early human ancestors, but during the lower Palaeolithic they disappeared, and the only hominin species found in fossilic records is Homo erectus for much of the Pleistocene. Acheulean lithics appear along with Homo erectus, some 1.8 million years ago, replacing the more primitive Oldowan industry used by A. garhi and by the earliest species of Homo. The Middle Paleolithic saw more varied speciation within Homo, including the appearance of Homo sapiens about 200,000 years ago.
According to mitochondrial timing techniques, modern humans migrated from Africa after the Riss glaciation in the Middle Palaeolithic during the Eemian Stage, spreading all over the ice-free world during the late Pleistocene. A 2005 study posits that humans in this migration interbred with archaic human forms already outside of Africa by the late Pleistocene, incorporating archaic human genetic material into the modern human gene pool.
The evolution of anatomically modern humans took place during the Pleistocene. In the beginning of the Pleistocene Paranthropus species are still present, as well as early human ancestors, but during the lower Palaeolithic they disappeared, and the only hominin species found in fossilic records is Homo erectus for much of the Pleistocene. Acheulean lithics appear along with Homo erectus, some 1.8 million years ago, replacing the more primitive Oldowan industry used by A. garhi and by the earliest species of Homo. The Middle Paleolithic saw more varied speciation within Homo, including the appearance of Homo sapiens about 200,000 years ago.
According to mitochondrial timing techniques, modern humans migrated from Africa after the Riss glaciation in the Middle Palaeolithic during the Eemian Stage, spreading all over the ice-free world during the late Pleistocene. A 2005 study posits that humans in this migration interbred with archaic human forms already outside of Africa by the late Pleistocene, incorporating archaic human genetic material into the modern human gene pool.
Miocene
The Miocene is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about 23.03 to 5.333 million years ago (Ma). The Miocene is preceded by the Oligocene and is followed by the Pliocene.
As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by a single distinct global event but consist rather of regionally defined boundaries between the warmer Oligocene and the cooler Pliocene Epoch.
During the Early Miocene, the Arabian Peninsula collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Ocean, and allowing a faunal interchange to occur between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans into Eurasia. During the late Miocene, the connections between the Atlantic and Mediterranean closed, causing the Mediterranean Sea to nearly completely evaporate, in an event called the Messinian salinity crisis. The Strait of Gibraltar opened and the Mediterranean refilled at the Miocene–Pliocene boundary, in an event called the Zanclean flood.
The apes first evolved, arose, and diversified during the early Miocene (Aquitanian and Burdigalian Stages), becoming widespread in the Old World. By the end of this epoch and the start of the following one, the ancestors of humans had split away from the ancestors of the chimpanzees to follow their own evolutionary path during the final Messinian Stage (7.5–5.3 Ma) of the Miocene. As in the Oligocene before it, grasslands continued to expand and forests to dwindle in extent. In the seas of the Miocene, kelp forests made their first appearance and soon became one of Earth's most productive ecosystems.
The plants and animals of the Miocene were recognizably modern. Mammals and birds were well-established. Whales, pinnipeds, and kelp spread.
The Miocene is of particular interest to geologists and palaeoclimatologists as major phases of the geology of the Himalaya occurred during the Miocene, affecting monsoonalpatterns in Asia, which were interlinked with glacial periods in the northern hemisphere.
The Miocene is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about 23.03 to 5.333 million years ago (Ma). The Miocene is preceded by the Oligocene and is followed by the Pliocene.
As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by a single distinct global event but consist rather of regionally defined boundaries between the warmer Oligocene and the cooler Pliocene Epoch.
During the Early Miocene, the Arabian Peninsula collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Ocean, and allowing a faunal interchange to occur between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans into Eurasia. During the late Miocene, the connections between the Atlantic and Mediterranean closed, causing the Mediterranean Sea to nearly completely evaporate, in an event called the Messinian salinity crisis. The Strait of Gibraltar opened and the Mediterranean refilled at the Miocene–Pliocene boundary, in an event called the Zanclean flood.
The apes first evolved, arose, and diversified during the early Miocene (Aquitanian and Burdigalian Stages), becoming widespread in the Old World. By the end of this epoch and the start of the following one, the ancestors of humans had split away from the ancestors of the chimpanzees to follow their own evolutionary path during the final Messinian Stage (7.5–5.3 Ma) of the Miocene. As in the Oligocene before it, grasslands continued to expand and forests to dwindle in extent. In the seas of the Miocene, kelp forests made their first appearance and soon became one of Earth's most productive ecosystems.
The plants and animals of the Miocene were recognizably modern. Mammals and birds were well-established. Whales, pinnipeds, and kelp spread.
The Miocene is of particular interest to geologists and palaeoclimatologists as major phases of the geology of the Himalaya occurred during the Miocene, affecting monsoonalpatterns in Asia, which were interlinked with glacial periods in the northern hemisphere.
Fauna
Both marine and continental fauna were fairly modern, although marine mammals were less numerous. Only in isolated South America and Australia did widely divergent fauna exist.
In the Early Miocene, several Oligocene groups were still diverse, including nimravids, entelodonts, and three-toed equids. Like in the previous Oligocene Epoch, oreodonts were still diverse, only to disappear in the earliest Pliocene. During the later Miocene mammals were more modern, with easily recognizable canids, bears, red pandas, procyonids, equids, beavers, deer, camelids, and whales, along with now extinct groups like borophagine canids, certain gomphotheres, three-toed horses, and hornless rhinos like Teleoceras and Aphelops. Islands began to form between South and North America in the Late Miocene, allowing ground sloths like Thinobadistes to island-hop to North America. The expansion of silica-rich C4 grasses led to worldwide extinctions of herbivorous species without high-crowned teeth.
Mustelids diversified into their largest forms as terrestrial predators like Ekorus, Eomellivora, and Megalictis and bunodont otters like Enhydriodon and Sivaonyx appeared.
Unequivocally recognizable dabbling ducks, plovers, typical owls, cockatoos and crows appear during the Miocene. By the epoch's end, all or almost all modern bird groups are believed to have been present; the few post-Miocene bird fossils which cannot be placed in the evolutionary tree with full confidence are simply too badly preserved, rather than too equivocal in character. Marine birds reached their highest diversity ever in the course of this epoch.
The youngest representatives of Choristodera, an extinct order of aquatic reptiles that first appeared in the Middle Jurassic, are known from the Miocene of Europe, belonging to the genus Lazarussuchus, which had been the only known surviving genus of the group since the beginning of the Eocene.
The last known representatives of the archaic primitive mammal order Meridiolestida, which dominated South America during the Late Cretaceous, are known from the Miocene of Patagonia, represented by the mole-like Necrolestes.
The youngest known representatives of metatherians (marsupial relatives) in the Northern Hemisphere landmasses (Asia, North America and Europe) and Africa are known from the Miocene, including the North American herpetotheriid Herpetotherium, the European herpetotheriid Amphiperatherium, the peradectidsSiamoperadectes and Sinoperadectes from Asia, and the possible herpetotheriid Morotodon from the late Early Miocene of Uganda.
Approximately 100 species of apes lived during this time, ranging throughout Africa, Asia and Europe and varying widely in size, diet, and anatomy. Due to scanty fossil evidence it is unclear which ape or apes contributed to the modern hominid clade, but molecular evidence indicates this ape lived between 18 and 13 million years ago.The first hominins (bipedal apes of the human lineage) appeared in Africa at the very end of the Miocene, including Sahelanthropus, Orrorin, and an early form of Ardipithecus (A. kadabba) The chimpanzee–human divergence is thought to have occurred at this time.
The expansion of grasslands in North America also led to an explosive radiation among snakes. Previously, snakes were a minor component of the North American fauna, but during the Miocene, the number of species and their prevalence increased dramatically with the first appearances of vipers and elapids in North America and the significant diversification of Colubridae (including the origin of many modern genera such as Nerodia, Lampropeltis, Pituophis and Pantherophis).
In the oceans, brown algae, called kelp, proliferated, supporting new species of sea life, including otters, fish and various invertebrates.
Cetaceans attained their greatest diversity during the Miocene, with over 20 recognized genera of baleen whales in comparison to only six living genera. This diversification correlates with emergence of gigantic macro-predators such as megatoothed sharks and raptorial sperm whales. Prominent examples are O. megalodon and L. melvillei. Other notable large sharks were O. chubutensis, Isurus hastalis, and Hemipristis serra.
Crocodilians also showed signs of diversification during Miocene. The largest form among them was a gigantic caiman Purussaurus which inhabited South America. Another gigantic form was a false gharial Rhamphosuchus, which inhabited modern age India. A strange form, Mourasuchus also thrived alongside Purussaurus. This species developed a specialized filter-feeding mechanism, and it likely preyed upon small fauna despite its gigantic size. The youngest members of Sebecidae, a clade of terrestrial crocodylfomes distantly related to modern crocodilians, are known from the Miocene of South America.
The last Desmostylians thrived during this period before becoming the only extinct marine mammal order.
The pinnipeds, which appeared near the end of the Oligocene, became more aquatic. A prominent genus was Allodesmus. A ferocious walrus, Pelagiarctos may have preyed upon other species of pinnipeds including Allodesmus.
Furthermore, South American waters witnessed the arrival of Megapiranha paranensis, which were considerably larger than modern age piranhas.
New Zealand's Miocene fossil record is particularly rich. Marine deposits showcase a variety of cetaceans and penguins, illustrating the evolution of both groups into modern representatives. The early Miocene Saint Bathans Fauna is the only Cenozoic terrestrial fossil record of the landmass, showcasing a wide variety of not only bird species, including early representatives of clades such as moas, kiwis and adzebills, but also a diverse herpetofauna of sphenodontians, crocodiles and turtle as well as a rich terrestrial mammal fauna composed of various species of bats and the enigmatic Saint Bathans Mammal.
Both marine and continental fauna were fairly modern, although marine mammals were less numerous. Only in isolated South America and Australia did widely divergent fauna exist.
In the Early Miocene, several Oligocene groups were still diverse, including nimravids, entelodonts, and three-toed equids. Like in the previous Oligocene Epoch, oreodonts were still diverse, only to disappear in the earliest Pliocene. During the later Miocene mammals were more modern, with easily recognizable canids, bears, red pandas, procyonids, equids, beavers, deer, camelids, and whales, along with now extinct groups like borophagine canids, certain gomphotheres, three-toed horses, and hornless rhinos like Teleoceras and Aphelops. Islands began to form between South and North America in the Late Miocene, allowing ground sloths like Thinobadistes to island-hop to North America. The expansion of silica-rich C4 grasses led to worldwide extinctions of herbivorous species without high-crowned teeth.
Mustelids diversified into their largest forms as terrestrial predators like Ekorus, Eomellivora, and Megalictis and bunodont otters like Enhydriodon and Sivaonyx appeared.
Unequivocally recognizable dabbling ducks, plovers, typical owls, cockatoos and crows appear during the Miocene. By the epoch's end, all or almost all modern bird groups are believed to have been present; the few post-Miocene bird fossils which cannot be placed in the evolutionary tree with full confidence are simply too badly preserved, rather than too equivocal in character. Marine birds reached their highest diversity ever in the course of this epoch.
The youngest representatives of Choristodera, an extinct order of aquatic reptiles that first appeared in the Middle Jurassic, are known from the Miocene of Europe, belonging to the genus Lazarussuchus, which had been the only known surviving genus of the group since the beginning of the Eocene.
The last known representatives of the archaic primitive mammal order Meridiolestida, which dominated South America during the Late Cretaceous, are known from the Miocene of Patagonia, represented by the mole-like Necrolestes.
The youngest known representatives of metatherians (marsupial relatives) in the Northern Hemisphere landmasses (Asia, North America and Europe) and Africa are known from the Miocene, including the North American herpetotheriid Herpetotherium, the European herpetotheriid Amphiperatherium, the peradectidsSiamoperadectes and Sinoperadectes from Asia, and the possible herpetotheriid Morotodon from the late Early Miocene of Uganda.
Approximately 100 species of apes lived during this time, ranging throughout Africa, Asia and Europe and varying widely in size, diet, and anatomy. Due to scanty fossil evidence it is unclear which ape or apes contributed to the modern hominid clade, but molecular evidence indicates this ape lived between 18 and 13 million years ago.The first hominins (bipedal apes of the human lineage) appeared in Africa at the very end of the Miocene, including Sahelanthropus, Orrorin, and an early form of Ardipithecus (A. kadabba) The chimpanzee–human divergence is thought to have occurred at this time.
The expansion of grasslands in North America also led to an explosive radiation among snakes. Previously, snakes were a minor component of the North American fauna, but during the Miocene, the number of species and their prevalence increased dramatically with the first appearances of vipers and elapids in North America and the significant diversification of Colubridae (including the origin of many modern genera such as Nerodia, Lampropeltis, Pituophis and Pantherophis).
In the oceans, brown algae, called kelp, proliferated, supporting new species of sea life, including otters, fish and various invertebrates.
Cetaceans attained their greatest diversity during the Miocene, with over 20 recognized genera of baleen whales in comparison to only six living genera. This diversification correlates with emergence of gigantic macro-predators such as megatoothed sharks and raptorial sperm whales. Prominent examples are O. megalodon and L. melvillei. Other notable large sharks were O. chubutensis, Isurus hastalis, and Hemipristis serra.
Crocodilians also showed signs of diversification during Miocene. The largest form among them was a gigantic caiman Purussaurus which inhabited South America. Another gigantic form was a false gharial Rhamphosuchus, which inhabited modern age India. A strange form, Mourasuchus also thrived alongside Purussaurus. This species developed a specialized filter-feeding mechanism, and it likely preyed upon small fauna despite its gigantic size. The youngest members of Sebecidae, a clade of terrestrial crocodylfomes distantly related to modern crocodilians, are known from the Miocene of South America.
The last Desmostylians thrived during this period before becoming the only extinct marine mammal order.
The pinnipeds, which appeared near the end of the Oligocene, became more aquatic. A prominent genus was Allodesmus. A ferocious walrus, Pelagiarctos may have preyed upon other species of pinnipeds including Allodesmus.
Furthermore, South American waters witnessed the arrival of Megapiranha paranensis, which were considerably larger than modern age piranhas.
New Zealand's Miocene fossil record is particularly rich. Marine deposits showcase a variety of cetaceans and penguins, illustrating the evolution of both groups into modern representatives. The early Miocene Saint Bathans Fauna is the only Cenozoic terrestrial fossil record of the landmass, showcasing a wide variety of not only bird species, including early representatives of clades such as moas, kiwis and adzebills, but also a diverse herpetofauna of sphenodontians, crocodiles and turtle as well as a rich terrestrial mammal fauna composed of various species of bats and the enigmatic Saint Bathans Mammal.